Dak Lak Tourism Guide 2025

Dak Lak is a province in the Central Highlands region of Vietnam, known as the "coffee capital" and the "land of elephants".
Planning a trip to Dak Lak province in Vietnam? This guide will help you discover the best places to stay, visit, and enjoy in this amazing destination. Learn more about Dak Lak’s geography, climate, tourism, and transportation here.
Overview
Dak Lak is a central highland area located in the mid-west of Vietnam. It has the fourth-largest area in Tay Nguyen. The place is home to a number of indigenous ethnic minorities such as M’nong, Rade, Jarai, and others. Dak Lak, in M’nong language, means Lak Lake.
Dak Lak is considered the cradle that nurturing the Central Highlands’s culture of Cong Chieng Tay Nguyen, which is recognized by UNESCO as an oral and intangible masterpiece of humanity recognized by the world.
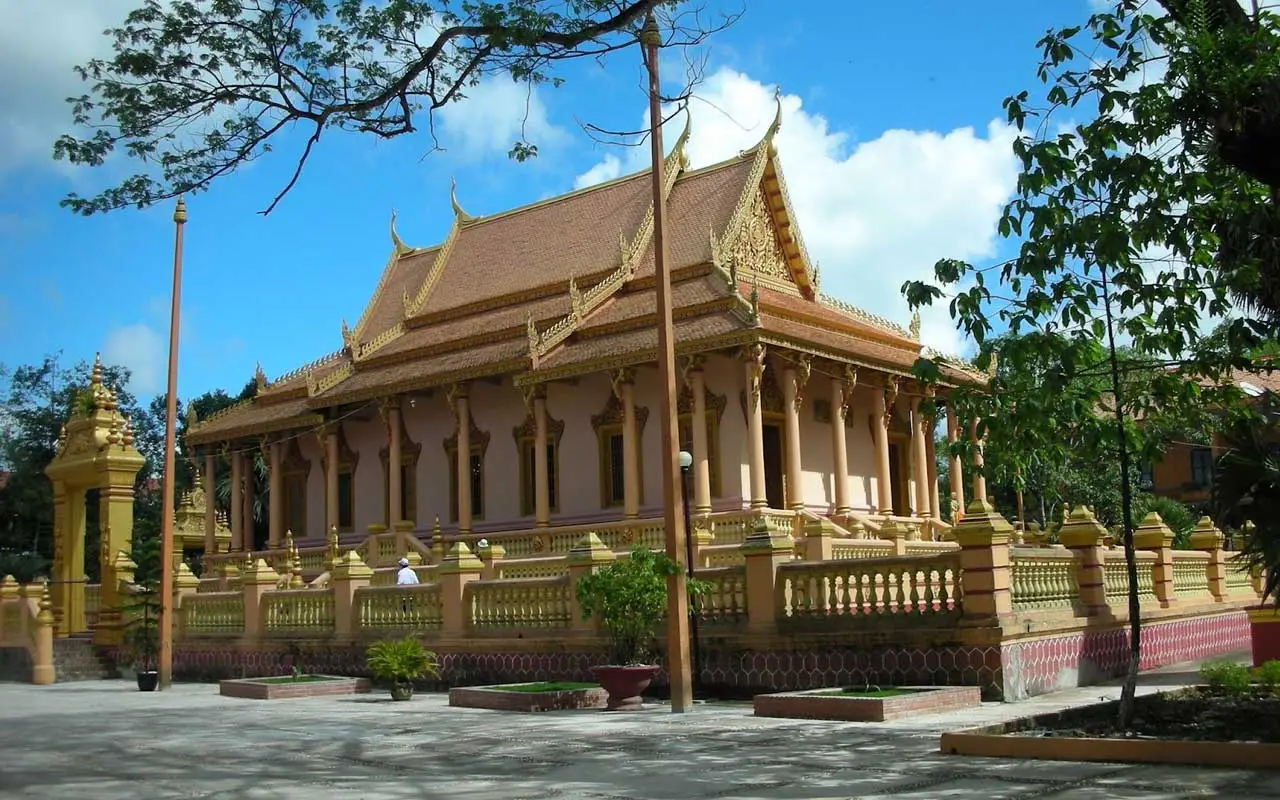
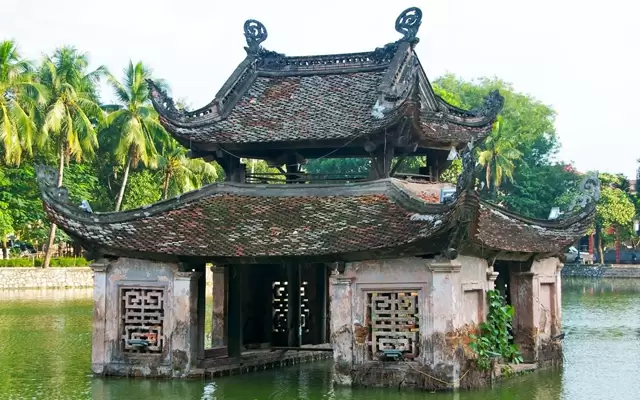
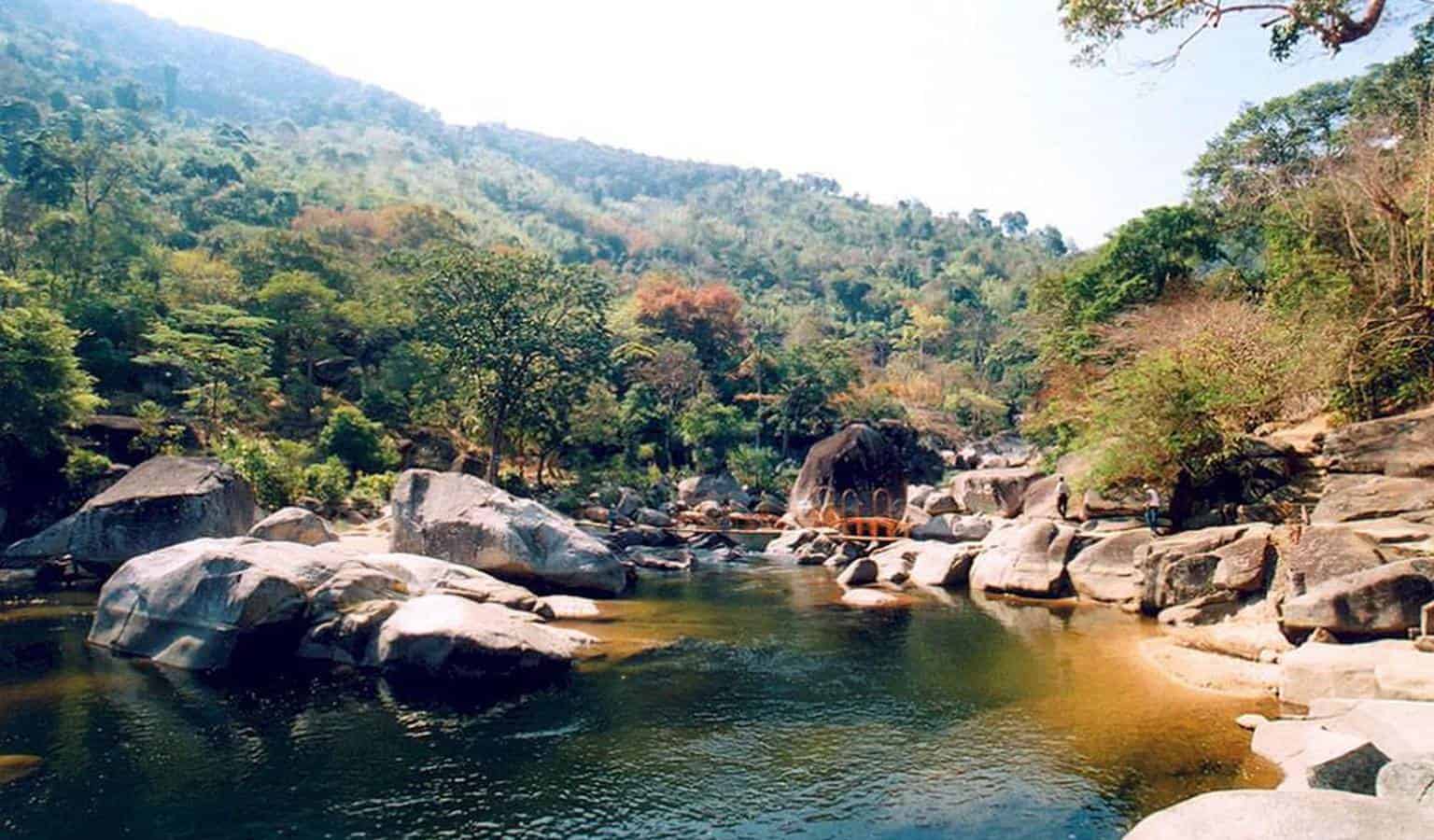
The province is famous for its natural landscapes and unique cultural identity. It features untouched waterfalls, forests, and villages; notably, Chu Yang Sin, and Yok Don are among the most beautiful hotspots. Buon Don in Dak Lak is also a popular destination for visitors to come and witness how the community lives and tames wild elephants.
- Area: 13.030,5 km²
- Population: 1.869.322 people
- Provincial Capital: Buon Me Thuot City
- Districts: 1 town and 12 suburban districts: Buon Don, Cu M’gar, Ea H’leo, Ea Kar, Ea Sup, Krông Ana, Krông Bông, Krông Búk, Krông Năng, Krông Pắk, Lắk, M’Đrắk.
History
Dak Lak was established under the command of the Governor-General of French Indochina in 1904. The province has gone through a number of merging and separations throughout history.
Until 2003, a part of Dak Lak was split into Dak Nong. Today, Dak Lak has one urban level 1 Buon Me Thuoc, and 13 suburban districts.
Geography
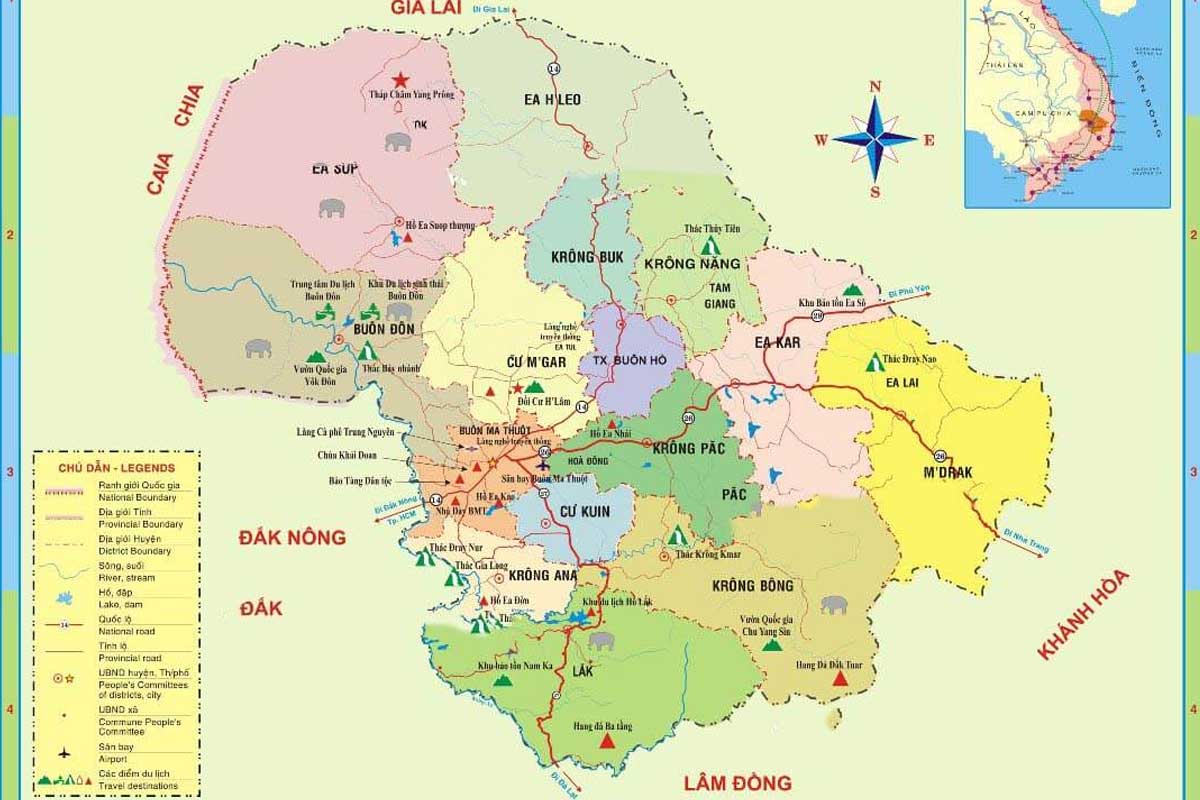
Dak Lak is located in the western part of the Central Highlands, bordering Gia Lai, Kon Tum, Lam Dong, Dak Nong and Cambodia. It has a total area of 13,125 km 2 and a population of about 1.9 million people.
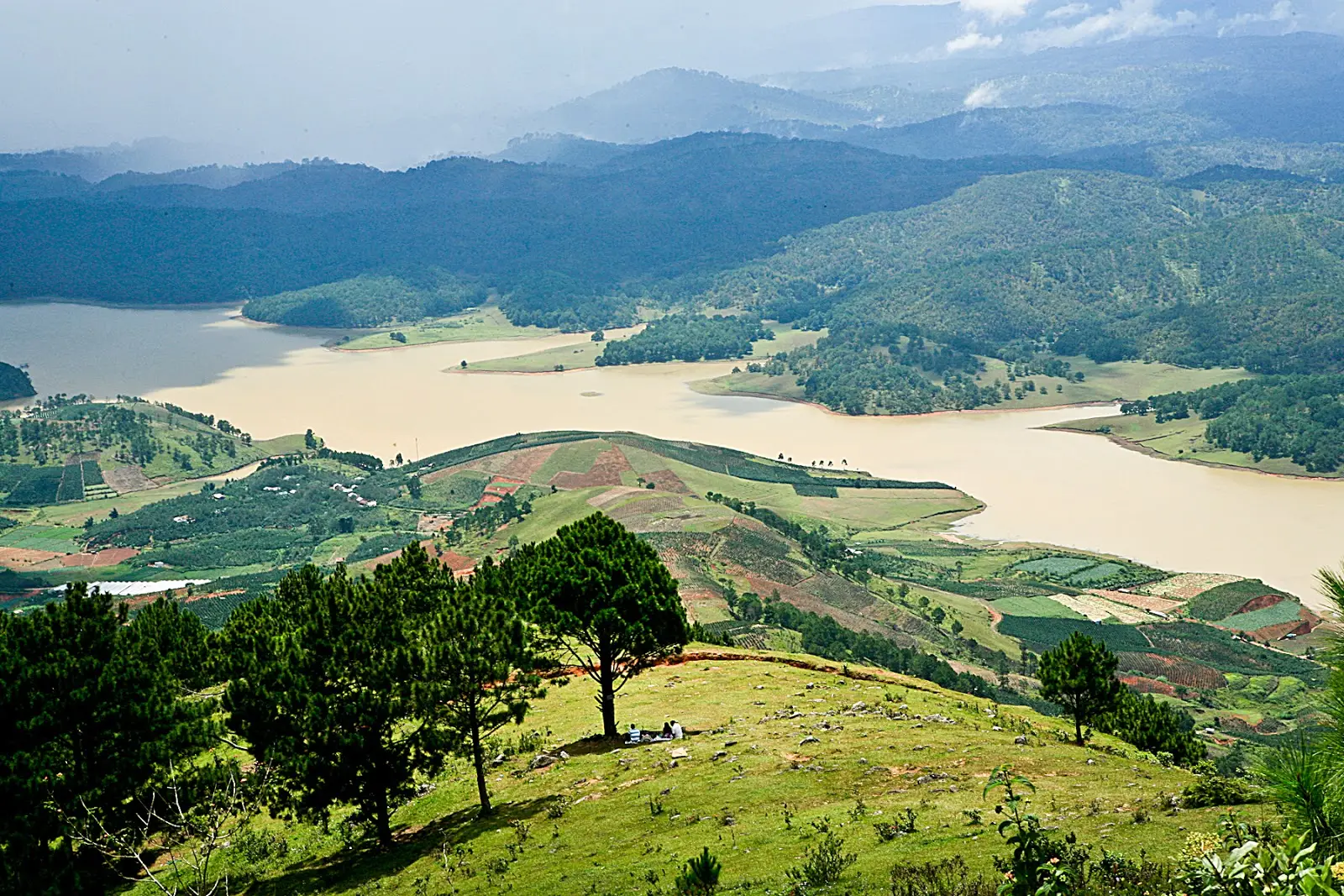
Dak Lak has typical mountainous topography as it’s located in the southwest of Truong Son mountain. It is the central province of Tay Nguyen with the north borders Gia Lai, east to Phu Yen, Khanh Hoa, south to Lam Dong, Dak Nong, and west to Cambodia.
The average height of 400-800 meters above sea level. The highest point is Chu Yang Sin mountain, which is 2442 m above sea level.
Climate
Dak Lak has a descending topography from southeast to northwest. Located at the west and the end of the Truong Son range is a large plateau with gently sloping terrain, quite flat alternating with low plains along the main river.
The province’s climate is divided into two subregions. The northwestern region has a hot, dry climate in the dry season, and the eastern and southern regions have a cool and moderate climate.
The rainy season usually starts from May to October with the prevailing southwest wind, the months with the highest rainfall are 7,8,9 months. During the dry season, the humidity decreases, the northeast wind blows, evaporates, causing severe drought.
Tourism

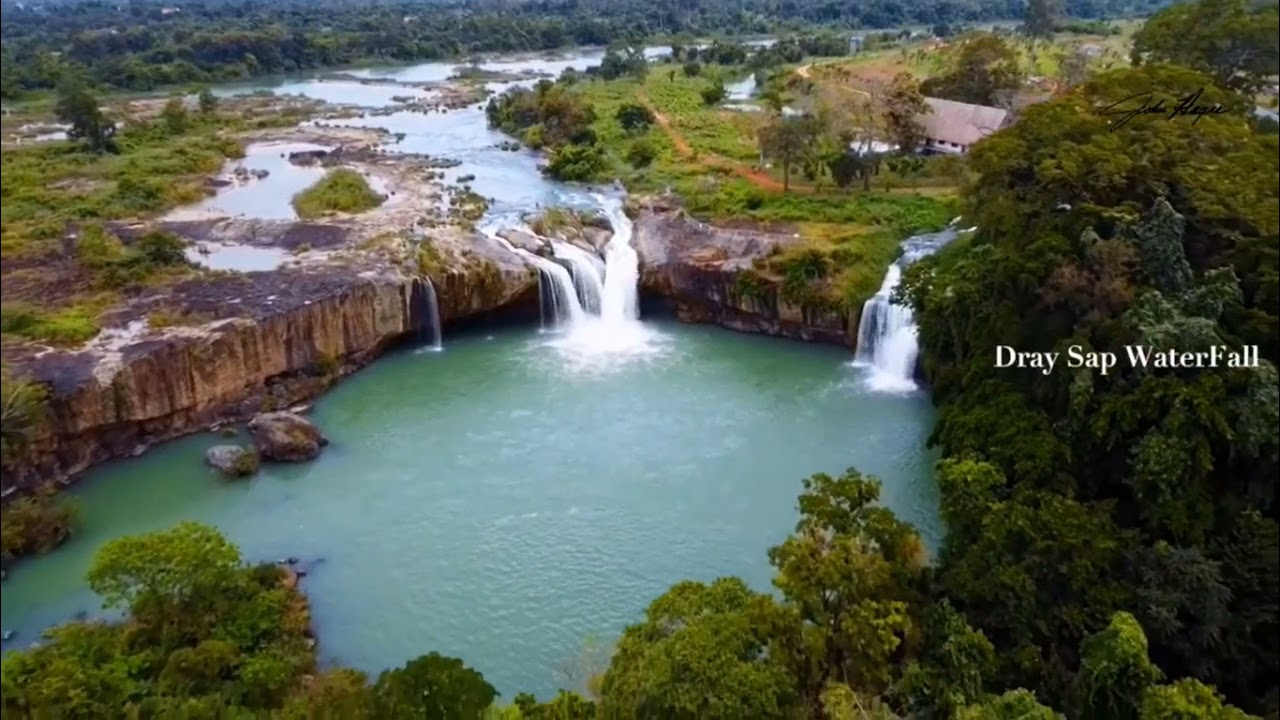
Dak Lak has many tourist attractions to offer, from natural wonders to cultural heritage. Some of the most popular destinations are Yok Don National Park, Dray Nur waterfall, Ethnographic Museum, and Ban Don elephant village.
The mountain province has a great advantage for tourism to grow. There are world-famous waterfalls with the wildest scene such as Gia Long, Trinh Nu, Krong Kmar, Ba Tang,…
Dak Lak is rich in culture and customs thanks to the presence of the multi-ethnical community.
Transportation
National highways cross Dak Lak from many central cities. No. 14 from Da Nang to Ho Chi Minh city, no. 28 to Phan Thiet, No. 27 to Da Lat.
Buon Ma Thuoc features an airport operating several routes from Da Nang, Ha Noi, and Ho Chi Minh City.