Vietnamese Art and 11+ Traditional Art Forms of Vietnam

Vietnam has a long and rich history, same as its art. Art of Vietnam reflects a mixture of influences from thousand year of Chinese domination and the French during the colonial periods. However, the way that keeps Vietnamese art to survive are its approach to foreign influences and incorporate their quintessence into its own culture. It is safe to say that, compare to other Asian countries, Vietnamese art has become one of the centers of attraction to the world’s art picture.

This post will provide more useful information about the art in Vietnam for your deeper understanding. Here we go!
Table of Contents
History of Vietnamese Art
Vietnamese art has undergone a long and rich history when its earliest examples dated back as far as the Stone Age around 8,000 BC. Followed by other important periods of history including Bronze Age, Chinese Domination (111 BC to 939 AD), Ngo to Tran Dynasty, the Fourth Chinese Domination and Le Dynasty, Nguyen Dynasty and Modern Art, Vietnamese art still keeps its long process of development until present.
Undoubtedly, Vietnamese art absorbed many Chinese influences from 2nd century BC until the 10th century AD. By the 19th century, the influences of French art gave a start in the birth of modern Vietnamese art. Together with these influences, art of Vietnam has always retained many distinctively Vietnamese characteristics.
Neolithic art (Stone Age)
The primitive clay pottery which was discovered in archaeological sites of Bac Son, Vietnam become the oldest artifact hailing from the Stone Age around 8,000 BC. The techniques for making stone objects in Neolithic era reached a sophisticated level with rhythmic designs reflecting original geometric thinking.
Bronze Age art
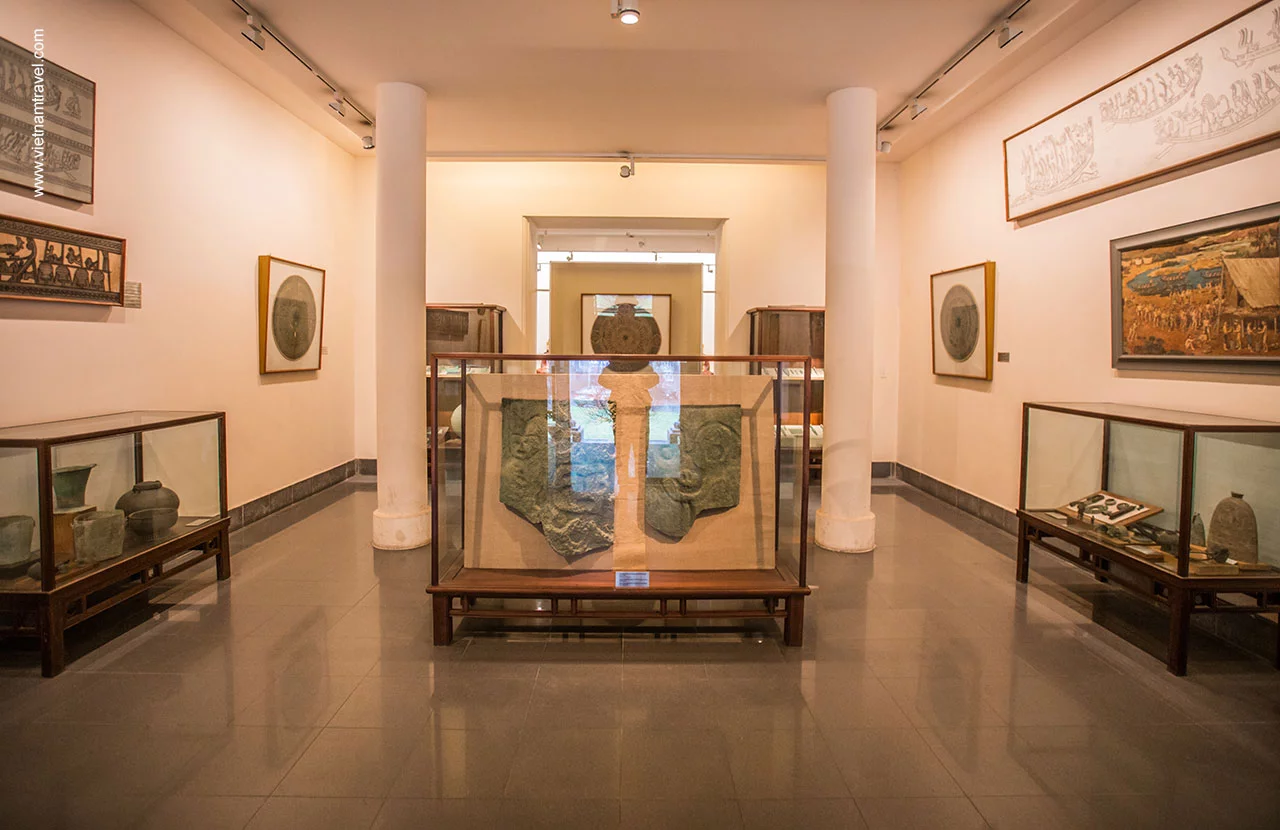

Vietnam National Fine Arts Museum
The techniques of decorating ceramics during 3 major stages in the development of ceramic art on the Bronze Age named Phung Nguyen, Dong Dau and Go Mun became the early models of decorative motifs on the bronze objects of the Dong Son civilization. The flourishing period of Dong Son culture in North Vietnam (from about 1,000 BC to the 4th century BC) was the civilization responsible for the world-famous Dong Son drums which gave us an important peek into early Vietnamese life.
Chinese Domination from 111 BC to 939 AD
During a millennium of Chinese domination, Vietnamese continued art production on native methods together with newly adapted techniques from Chinese in making ceramics. From the excavation of Chinese tombs, it can be seen and proven. The level of techniques in the products in this period was also sophisticated with the introduction of potter’s wheel and the use of a thin yellow or white glaze to cover thick-walled ceramics.
From the Ngo to Tran Dynasty
During this period of national independence, Vietnamese art and ceramics were considered to be a thriving stage with the significant influences of the ancient native styles, the Celadon porcelain tradition of the Song from China and the style of Tam Thai (three colors) ceramics under Tang Dynasty. Vietnamese art also adopted Chinese-influenced philosophies, such as Confucianism, Mahayana Buddhism and Taoism. Small traces of Cham influences were found as well.
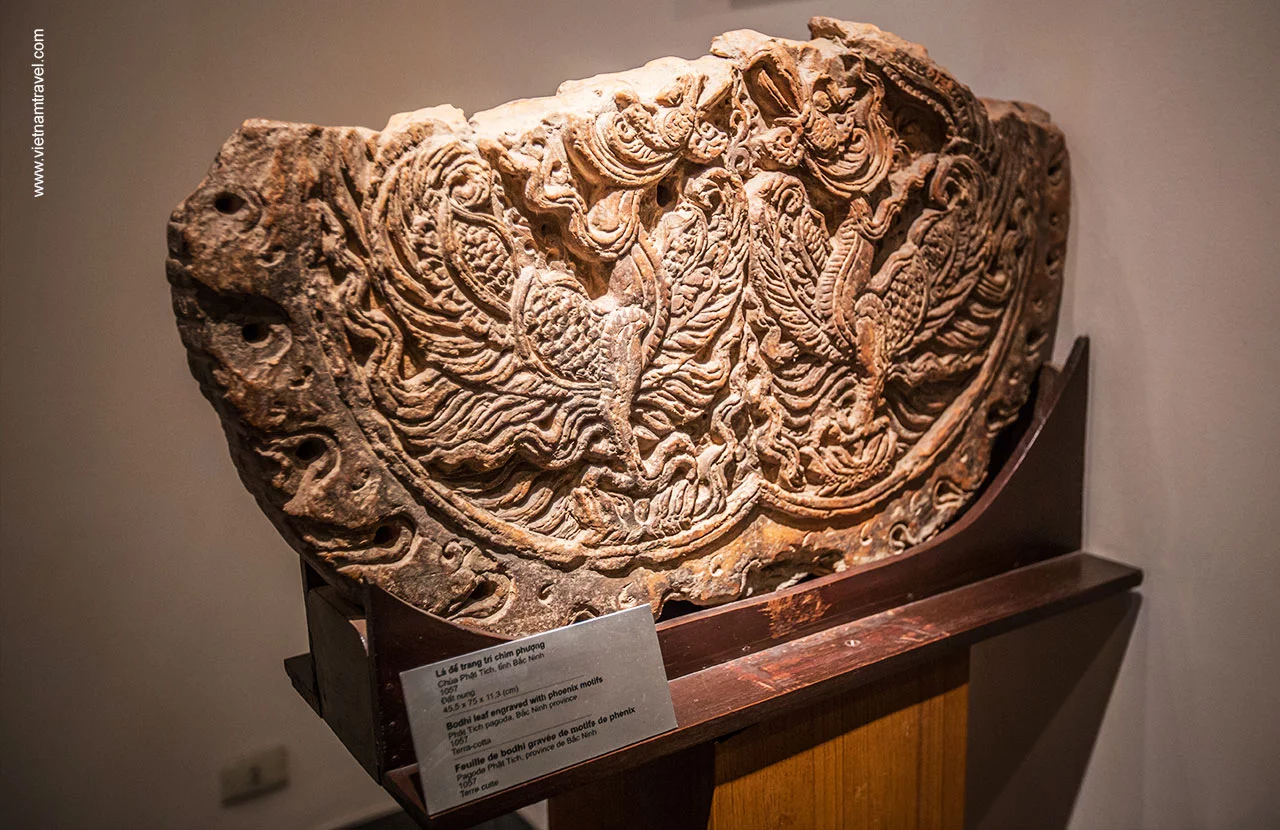

The display of Bodhi leaf engraved with phoenix motifs at Phat Tich Pagoda
Under Ly Dynasty (1010 to 1225), Vietnamese ceramics underwent a period of creation with main changes in the design, such as: slender in shape and covered with an emerald glaze in different colors, leading its ceramics become famous across East and Southeast Asia.
In this reign, many constructions of Vietnam’s landmark structures were born, such as One Pillar Pagoda, the Temple of Literature or Quynh Lam Pagoda.
The Tran Dynasty (1225-1400) followed with a more subdued approach to art. A large number of pottery villages with their specialized products were found in Bat Trang (Hanoi City), Tho Ha (Bac Giang Province) and Phu Lang (Bac Ninh Province).
The Fourth Chinese Domination and Le Dynasty
Despite lasting only about 2 decades, the fourth Chinese domination was seen as the harshest dominating period to Vietnamese people. Many if not most all of classical Vietnamese books were burnt as well as much documentation of the era of independence was lost. Countless Vietnam resources and artifacts were taken to China. In this period, the Ming artistic tradition heavily influenced in many art forms of Vietnam.
Nguyen Dynasty
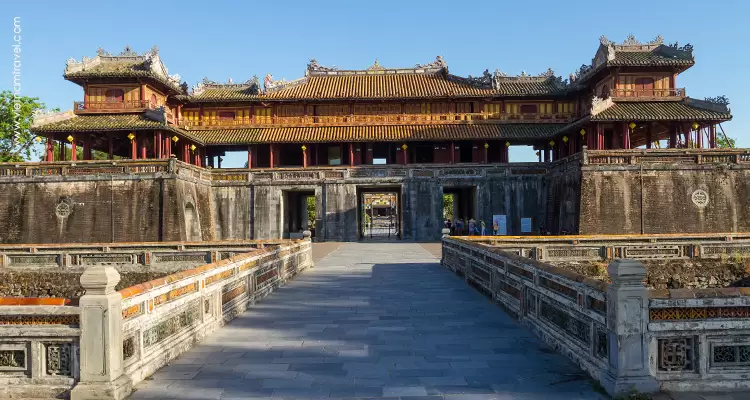

This was the last ruling dynasty of Vietnam, but revived interest in ceramics and porcelain. In addition, the powerful presence of the performing arts, such as imperial court music and dance was seen during this period. However, at the latter part of the Nguyen Dynasty, other forms of arts experienced a catastrophic decline.
Modern Art
Vietnamese Art was considerably influenced by French artistic style at the beginning of the 19th century, mostly thriving in big cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
In 1925, Fine Arts College of Indochina, or Ecole des Beaux-Art de l’Indochine, was established by French artist – Victor Tardier in Hanoi, and French techniques started to be utilized by modern Vietnamese artists in many traditional materials which creates a unique blend of eastern and western elements, drawing the interest of the international art market, especially in France and other countries in Europe.
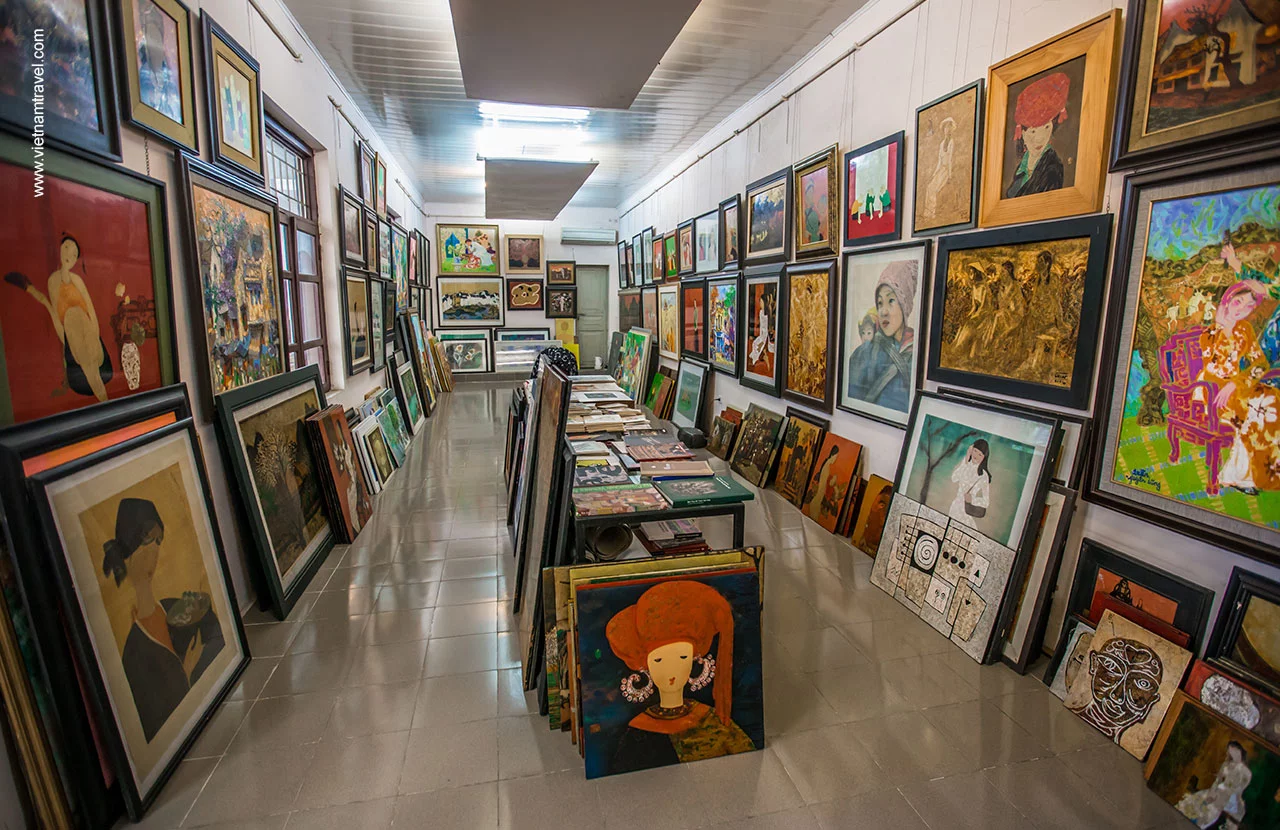

Art gallery with the variety of colors, forms and contents
From here, many pioneers of Vietnamese modern art also appeared. Some famous names can be listed as below:
For Oil Painting: To Ngoc Van, Nam Son, Le Pho, Tran Van Can, Nguyen Gia Tri, Bui Xuan Phai, Phan Ke An …
For Silk Painting: Nguyen Phan Chanh, Nam Son, Nguyen Sy Ngoc, Nguyen Trong Hop…
For Lacquer: Song Van Trung, Pham Hau, Nguyen Hang, Tran Van Can, Nguyen Gia Tri, Nguyen Sy Ngoc, Phan Ke An…
For Watercolor: Nam Son, Hoang Lap Non (ink), Nguyen Sy Ngoc, Nguyen Trong Hop…
For Woodcut Art: An Son Do, Duc Thuan, Pham Van Don…
For Gouache and Pastel: Le Thi Luu (pastel), Nguyen Do Cung, Nguyen Dung (pastel), Nguyen Tien Chung, Ta Thuc Binh, Bui Xuan Phai, Le Thanh Duc, Mai Van Hien, Van Cao…
Vietnamese artists successfully added Asian themes and their personal styles into the art works. We can see that many same names appear twice or more in various categories, not specific to one type only. That shows the multi-talent and great quality of Vietnamese artists.
Read more: Van Phuc Silk Village
Vietnamese Art Forms
During the long process of development, there are numerous works of art found in archeological sites throughout the country with many types including sculptures, ceramics, paintings… and a variety of materials, such as stone, bronze, steel, clay, wood, and paper. Besides, other art forms have been developed to satisfy Vietnamese demand for enjoying art and entertainment, such as architecture, calligraphy, visual arts, performing arts, language arts, cinemas…
Architecture
Thanks to depicted patterns on the bronze Dong Son drums, it is believed that in prehistoric times, Vietnamese people lived in stilt-houses which are similar to some kinds of houses found in Vietnam today.
During the domination of China, Chinese architecture had a large influence on the structures of many types of Vietnamese buildings, mainly pagodas and temples, communal houses, imperial palaces and quarters, but still create the harmonious combination of Vietnamese traditional style and Chinese architecture.
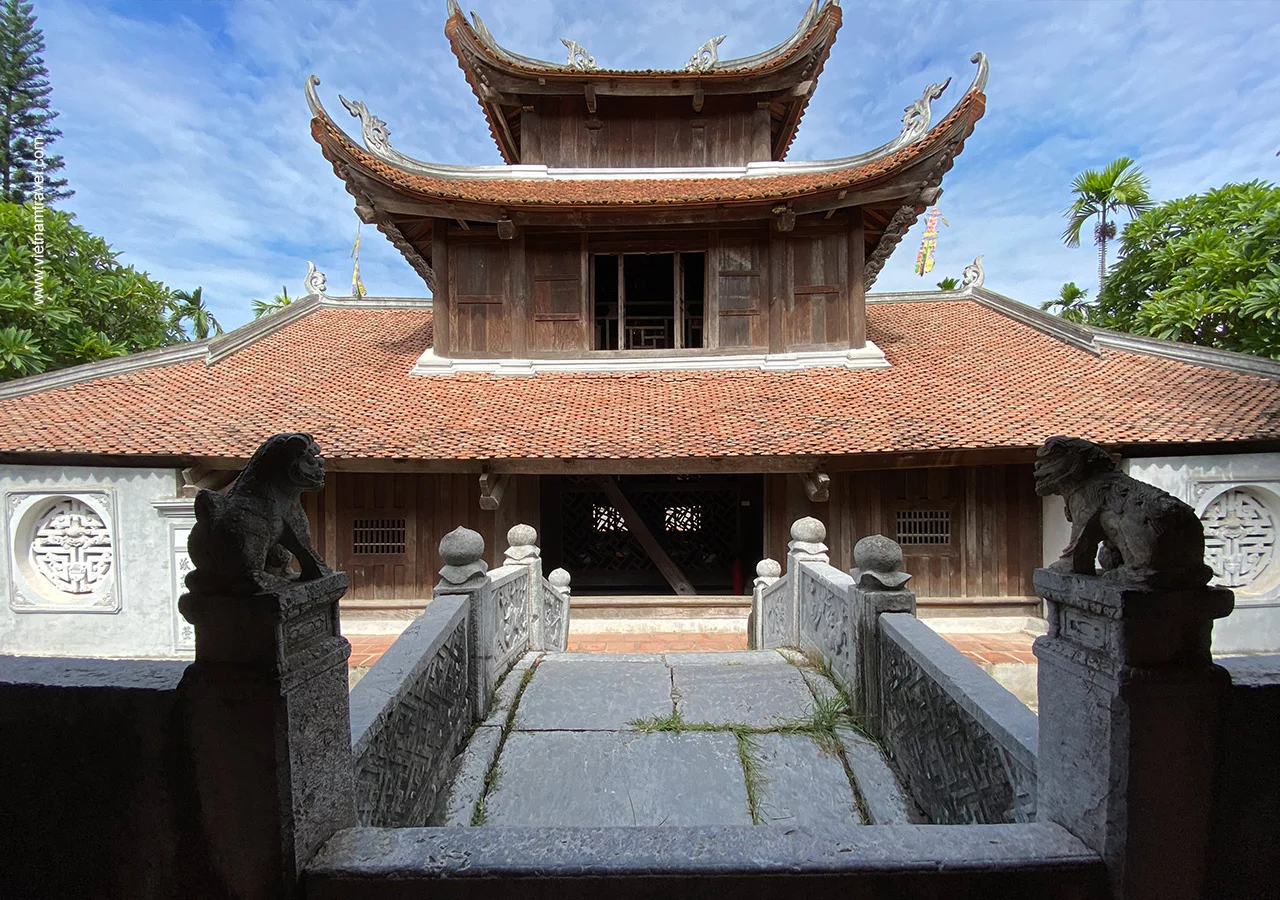

Tich Thien Am pavillon (connected with the Main Hall by a stone bridge across the lotus lake) at But Thap Pagoda
When French colonists landed into Vietnam in the 19th century, numerous French-styled architectural structures were constructed, including villas, government buildings, churches, opera houses…
Here are some of Vietnam’s most notable architectural complexes that stand still with their beauty and attraction nowadays, including the Temple of Literature, One Pillar Pagoda, Hue Imperial City, Perfume Pagoda (Chua Huong) and many other French architectural style buildings throughout the country.
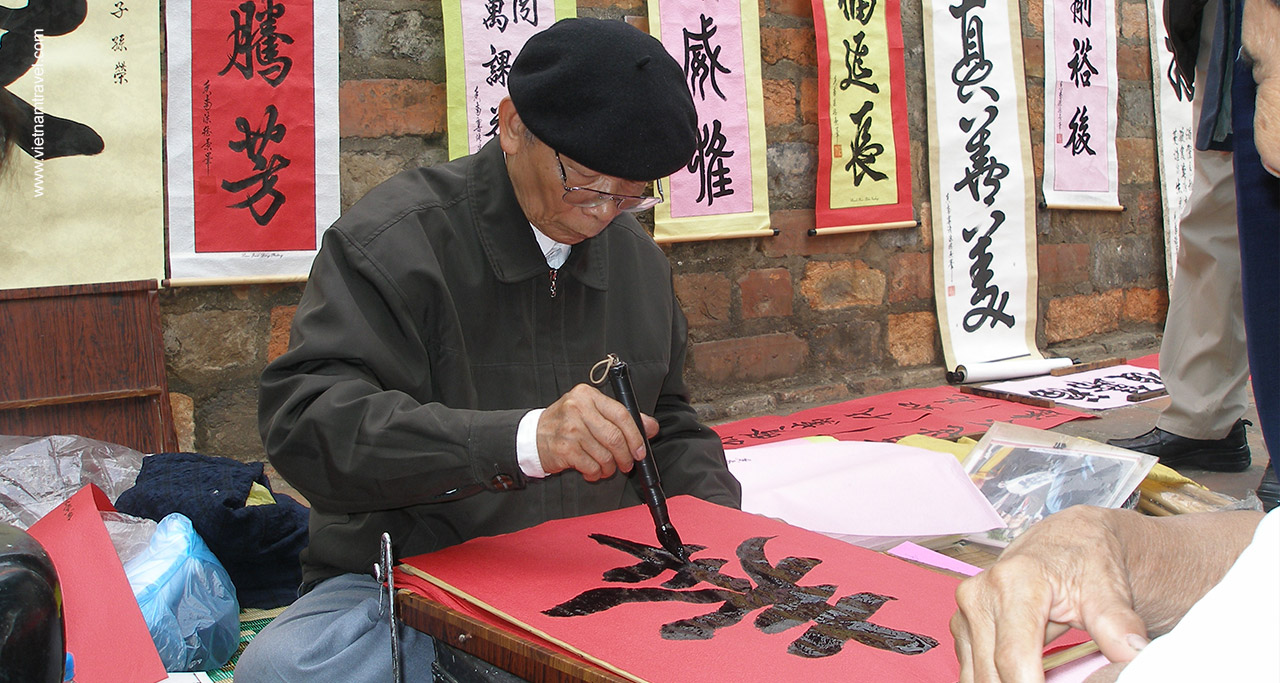
Calligraphy
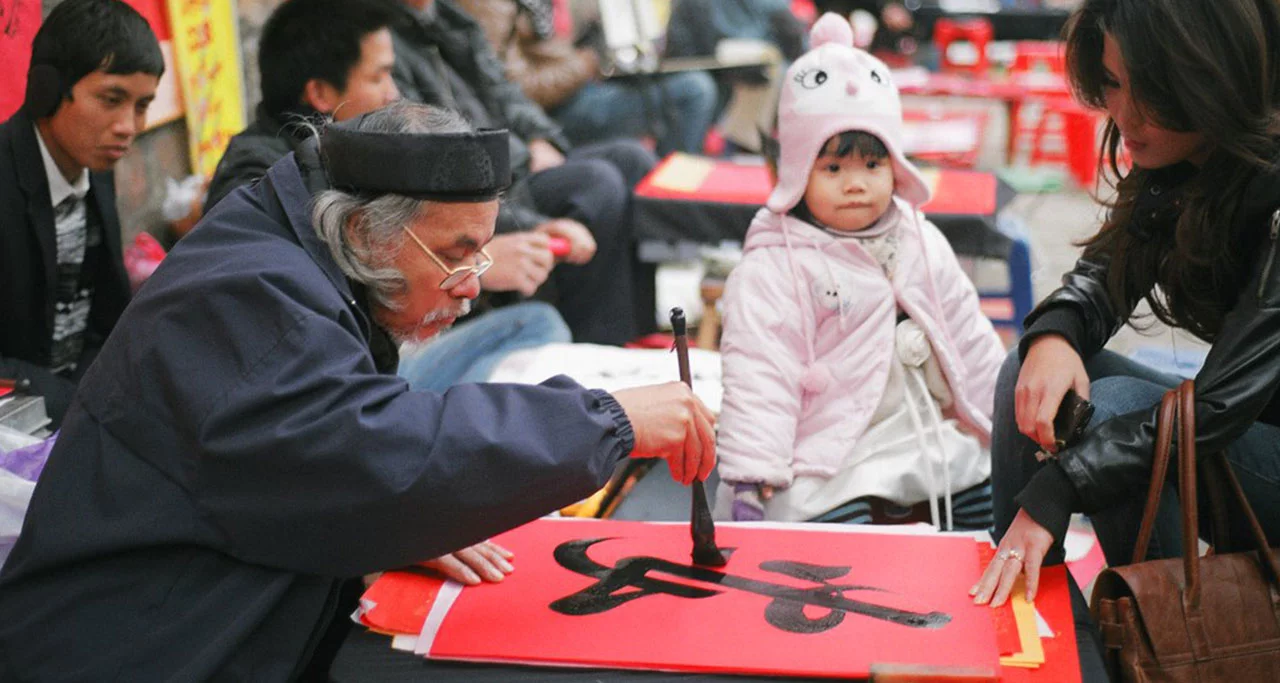

Calligraphy can be roughly translated as “the rule of writing” or other called “Thu Phap”. In Vietnam, calligraphy is one of the most treasured art forms which shows the calligrapher’s feeling and their inner voice in each character.
Traditional Vietnamese calligraphy is strongly affected by Chinese calligraphy’s standard and uses Han script (Chinese language) in many of its writings. During the Ly Dynasty, its style was similar to China’s Tang Dynasty (618 – 907) while writing in Tran Dynasty was influenced by China’s Song (960-1279) and Yuan (1271-1368) Dynasties.
Over the time, Vietnam developed its own styles of calligraphy for writing both Han script and Nom script.
Nowadays, the old Vietnamese character-based writing systems are replaced with Quoc Ngu, a script based on the Latin alphabet with accent mark under each character which gained popularity during the New Poetry and Free Poetry Movements. However, calligraphy still plays a significant role in Vietnamese life. Especially on Tet holiday, calligraphy becomes a tradition of giving. It is believed that getting a calligraphy hanging from a scholar means bringing luck, health and wealth to the family.
Visual Arts
Traditional Silk Paintings & Woodblock prints
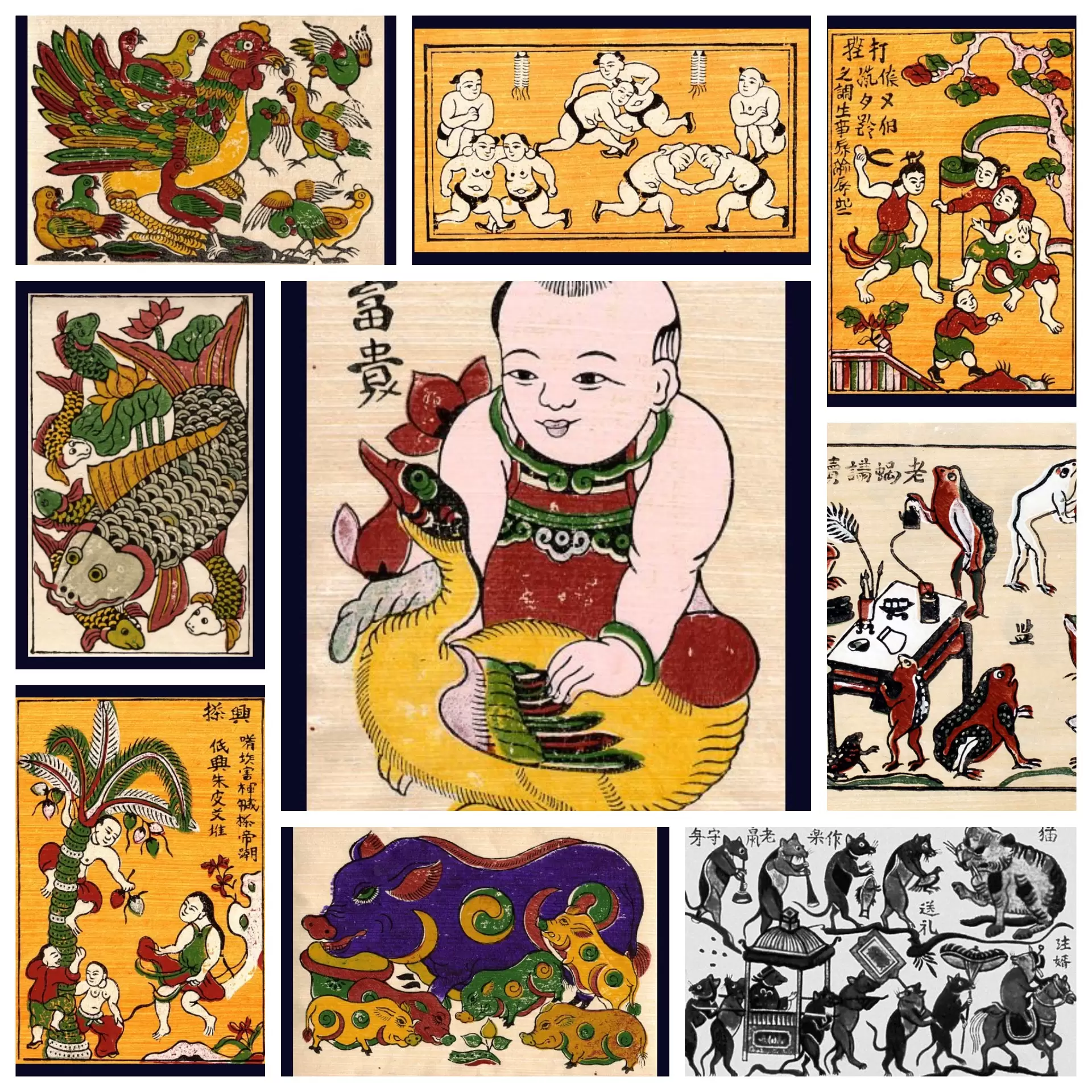 The Vietnamese silk paintings are one of the most popular forms of art, typically depicted the countryside, landscapes, pagodas, scenes of daily life and historical events. These artworks were transformed under the French influence with more liberality and modern, especially in the aspect of color.
The Vietnamese silk paintings are one of the most popular forms of art, typically depicted the countryside, landscapes, pagodas, scenes of daily life and historical events. These artworks were transformed under the French influence with more liberality and modern, especially in the aspect of color.
Much like the woodblock prints. To make this type of paintings, the artists will use organic materials to apply into the wood and press on paper. The process will be repeated with different colors until the final result is completed. Dong Ho Painting is the typical one of this famous art form.
Some other kinds of art forms for paintings can be listed, such as oil paintings, lacquer paintings, watercolor paintings, Gouache and Pastel paintings.
Sculpture
Vietnamese sculpture in traditional art has had a significant development which strongly influenced by 3 traditional religions: Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism coming from China and India. Examples of Vietnamese sculpture at early stage can be found in common houses, temples, and pagodas.
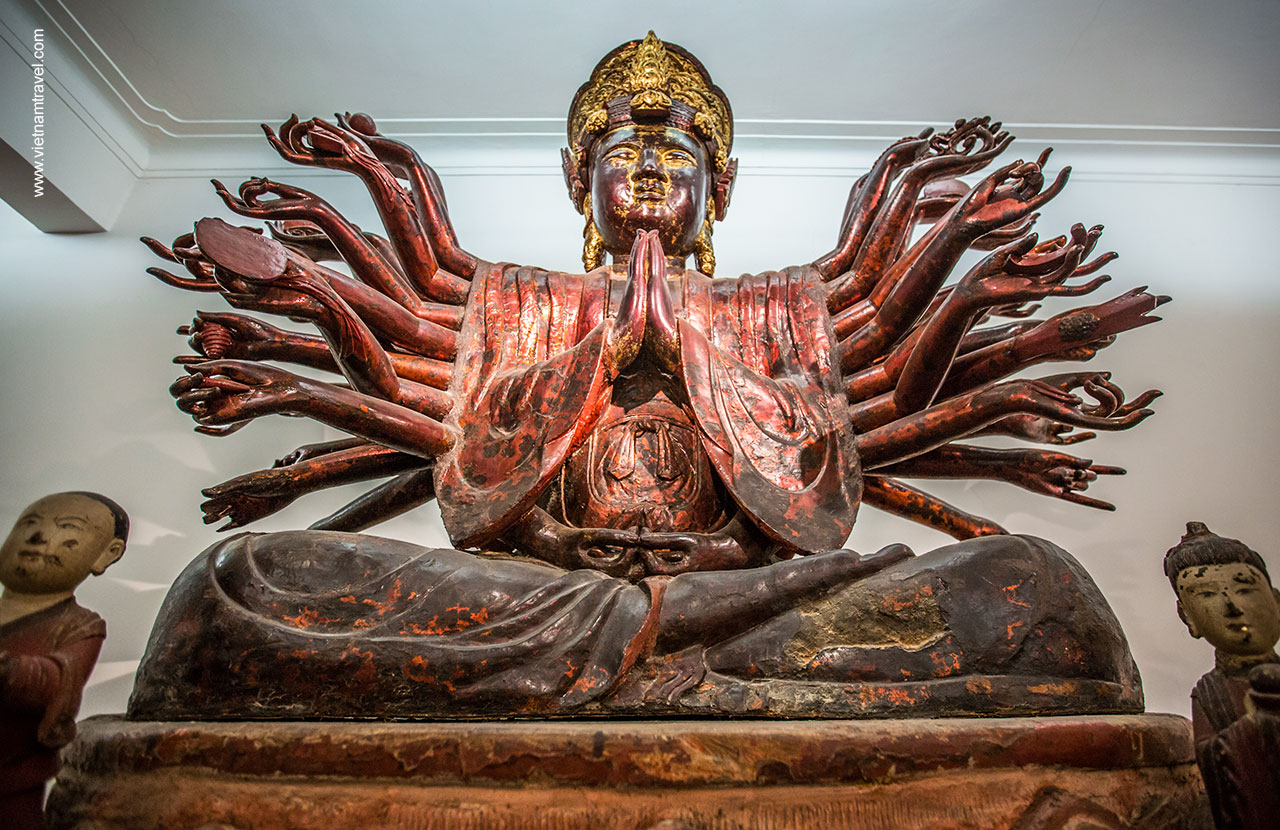

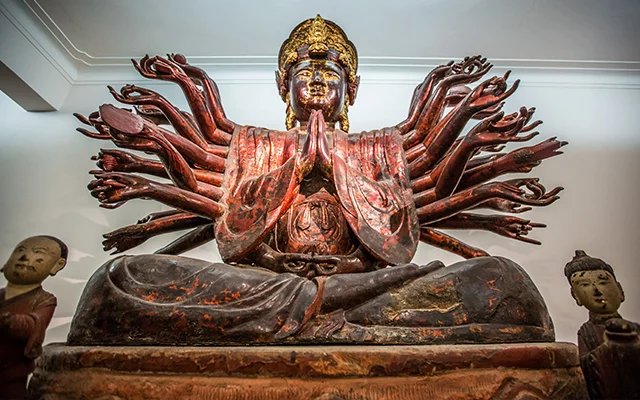
Statue of Bodhisattva Avalokisteshvara (national treasure) at Vietnam National Fine Arts Museum
The main categories of Vietnamese sculpture can include that of the Funan and Champa kingdoms in Southern Vietnam; the Chams in Central Vietnam; the Dai Viet in the North of Vietnam, and the Grave Houses in the Central Highlands.
Photography
In the middle of 19th century, photographic technology was introduced to Vietnam by French and Chinese commercial photographers. Since then, there was a diverse range of photography practices such as fine art photography, documentary photography, and landscape photography. The development of such practices have been accelerated following the economic reforms in Vietnam in 1986 which resulted in a diversification of funding for artists and increased international exposure.
Ceramic and Pottery
Vietnamese ceramic and pottery have a long history spanning from Bronze Age, Sa Huynh and Dong Son culture, then followed with Chinese influence. When Thang Long (Hanoi) became the capital, jade-glazed ceramics coming from Hanoi reached international acclaim across East Asia for the next 200 years. The Tran Dynasty followed the Ly Dynasty to continue a legacy of pottery making in northern Vietnam. During this time, the center of production was moved from Hanoi to Thanh Hoa, and the style of pottery was changed from green glaze to iron brown.
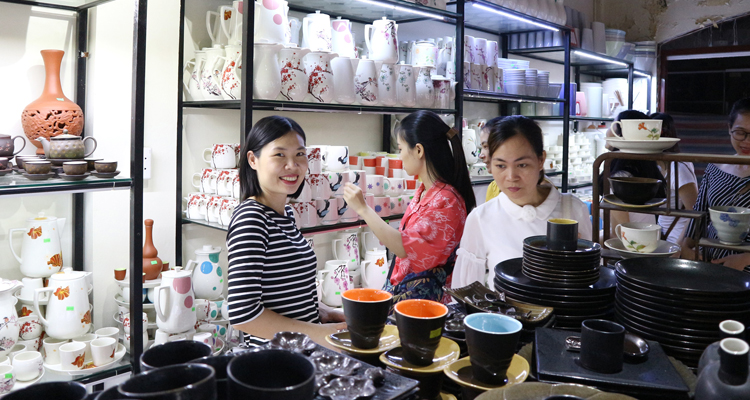

The variety of ceramic products at Bat Trang ceramic village
In Nguyen Dynasty, Vietnam found a style that it would stick with to the present day.
Nowadays, visitors can buy qualified products of this art forms in traditional villages such as Bat Trang (Hanoi), Phu Lang (Bac Ninh), Thanh Ha (Hoian), Bau Truc (Ninh Thuan), Bien Hoa (Dong Nai), Vinh Long (Mekong Delta), etc.
Read more: Bat Trang Ceramic Village
Hand Embroidery
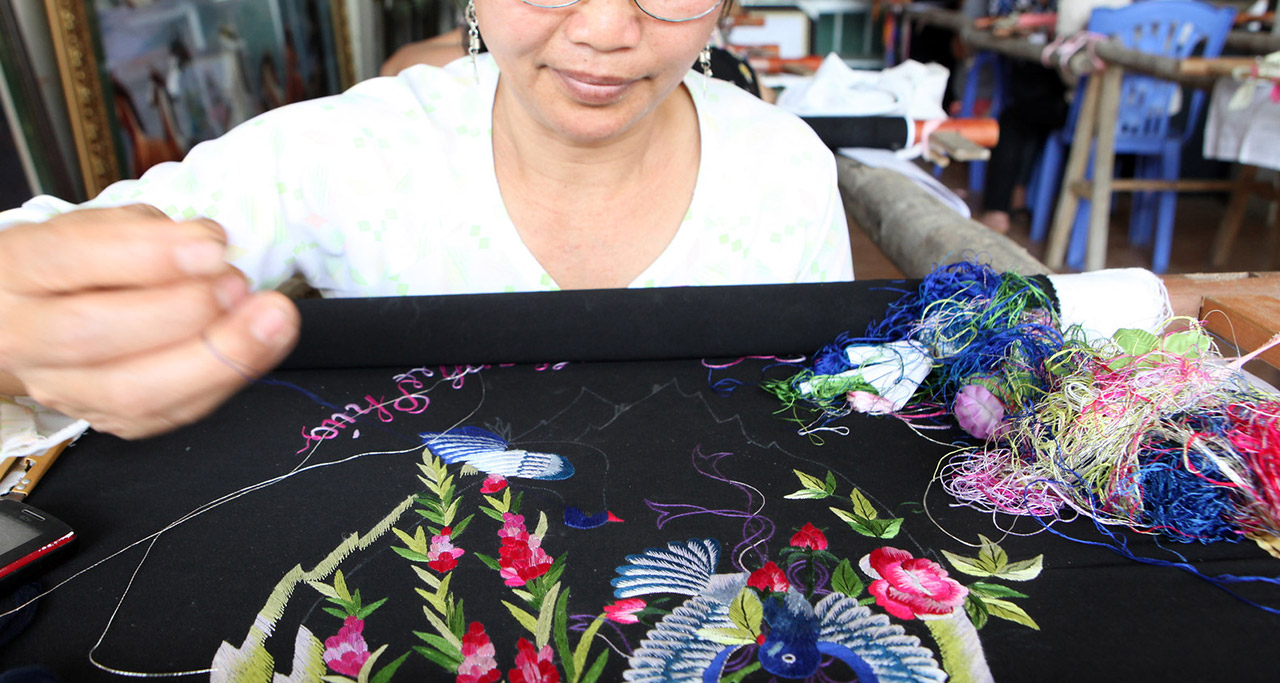

Hand embroidery is another type of Vietnam art form which embedded in Vietnamese culture dating back more than 700 years. This form is kept alive in modern times by local artisans, ethnic minorities and artists with dominant themes such as flowers, animals, landscapes and religious scenes. By using the tiny threads to create fine lines and mix of vibrant colors, there are various decorative accessories made from, such as pillowcases, tablecloths, and even silk embroidered paintings.
Lacquerware and Hoian Lanterns
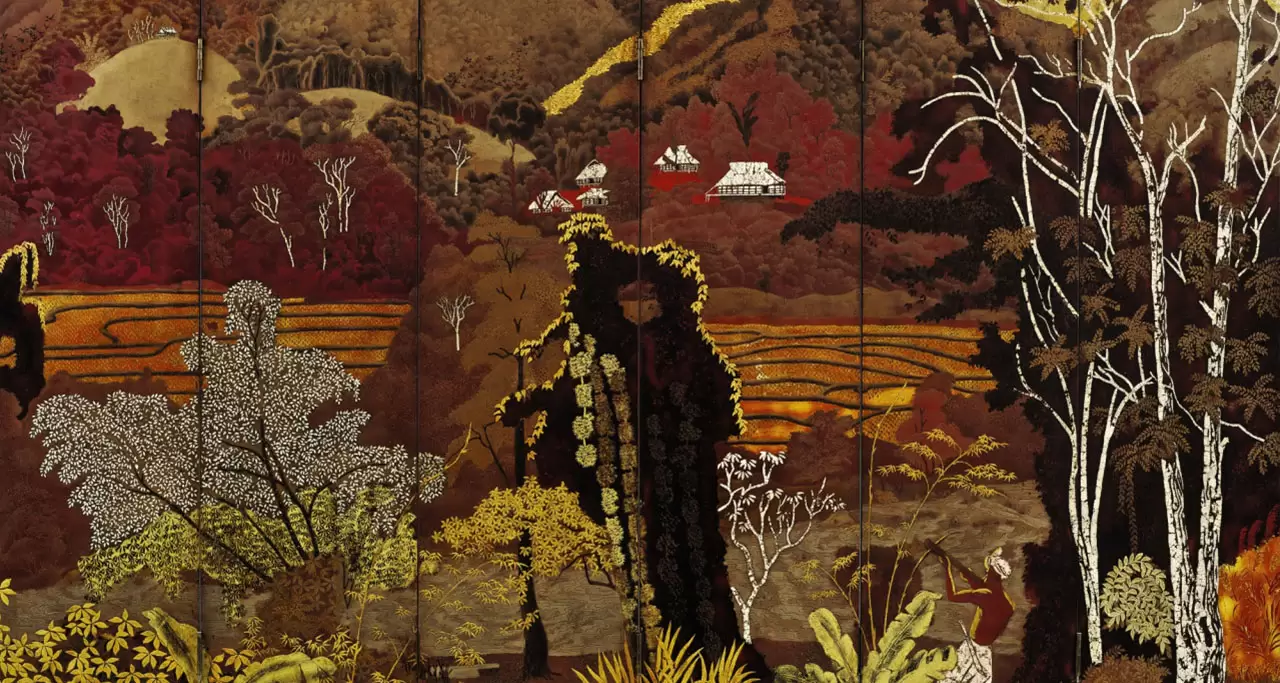

As a traditional fine art, Vietnamese lacquerware was handed down from generation to generation as a family secret until when Indochina Fine Arts school in Hanoi was born, which made the big renovation by excellent artists. New materials were discovered to create more eye catching and better qualified products. High-gloss lacquer is usually applied to a wooden base with inlays such as duck egg shells, gold or silver leaves.
Hoian Ancient town (Central Vietnam) is famous with its beautiful lanterns in different shape, size and color. Visitors can see myriad lanterns everywhere, especially in night time, the town becomes more magical with thousands of lanterns reflecting their light on the river. This is really an attractive art form that appealing the attention from anyone to come.
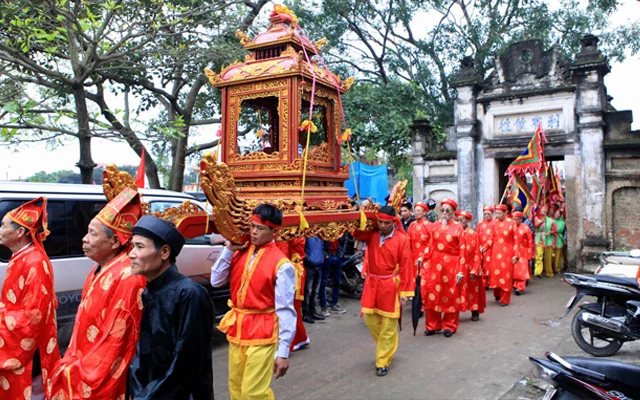
Performing Arts
Traditional Music
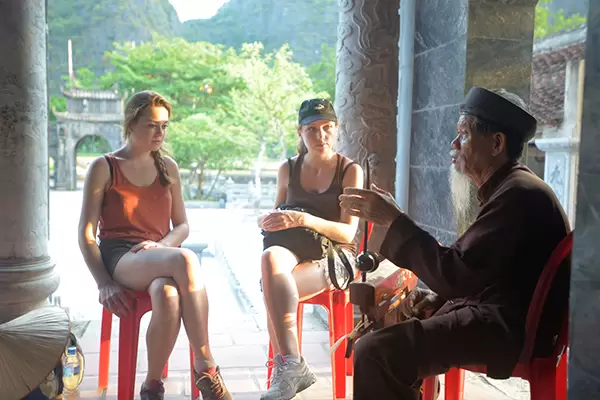

Old artist plays traditional instrument to foreign visitors
In the old days, Vietnamese traditional music developed rapidly, consisting of many different styles varying from region to region together with the emergence of numerous music instruments. These music genres hold an important part in the daily life of Vietnamese. It was as a tool to express the innermost feelings, to encourage people in working and fighting, to educate the children in good traditions and national sentiment, to communicate with the ancestors, and to sublimate the aspirations for a happy life. There are some widely known lists of traditional music which have been already recognized as Vietnam’s Human Intangible Cultural Heritage by UNESCO, such as Imperial Court music (2008), the Space of Gong Culture in the Central Highlands (2008), Quan Ho sing (2009), Ca Tru singing (2009), Xoan singing (2011), Don Ca Tai Tu (2013), Vi-Giam singing (2014)…
Traditional Theater
Despite being strongly influenced by Chinese opera and other art forms, Vietnamese theaters have been modified to be suitable for Vietnamese people with three special genres: Tuong singing, Cheo singing và Cai Luong singing.
Traditional Dance
With 54 different ethnics throughout the country, each ethnic community of Vietnam will feature their own traditional dance. Among of them include several traditional dances such as lion dance are widely performed at festivals and other special occasions like opening ceremonies…
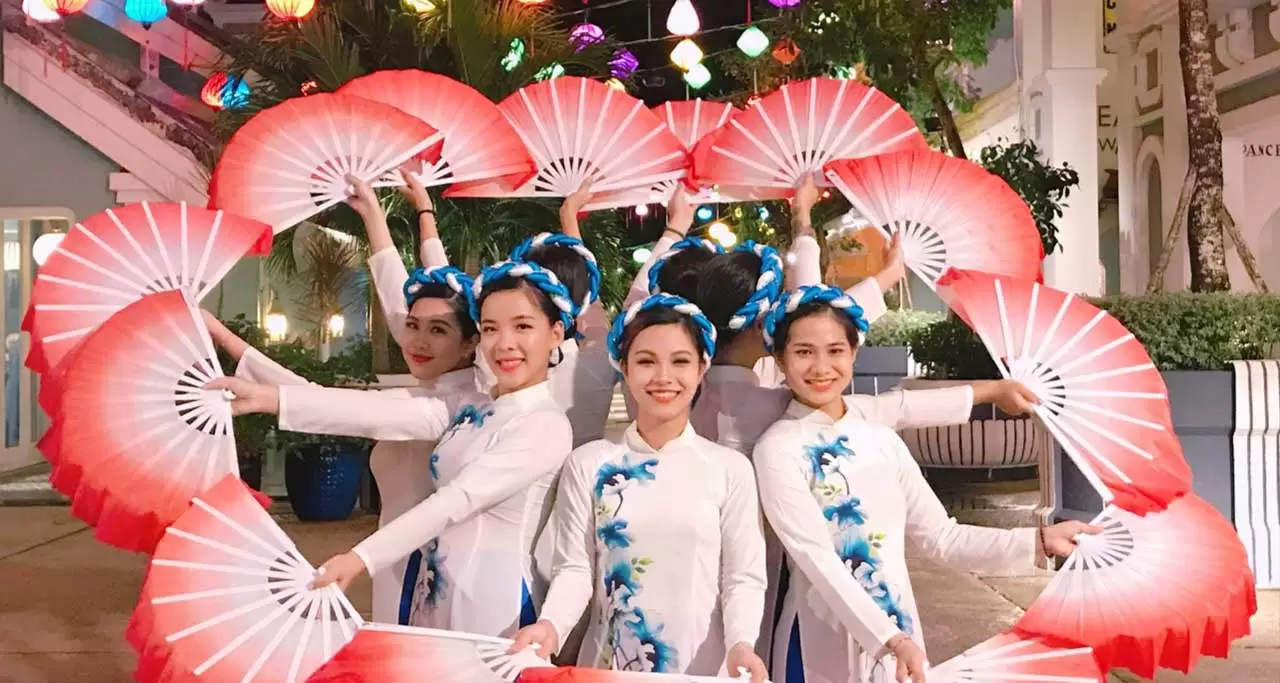

The grace of young artists in the fan dance with traditional dress
In the imperial court, a series of complex court dances which require great skills are also developed throughout the centuries, in which, the more widely known types are the imperial lantern dance, fan dance, and platter dance.
Water puppetry
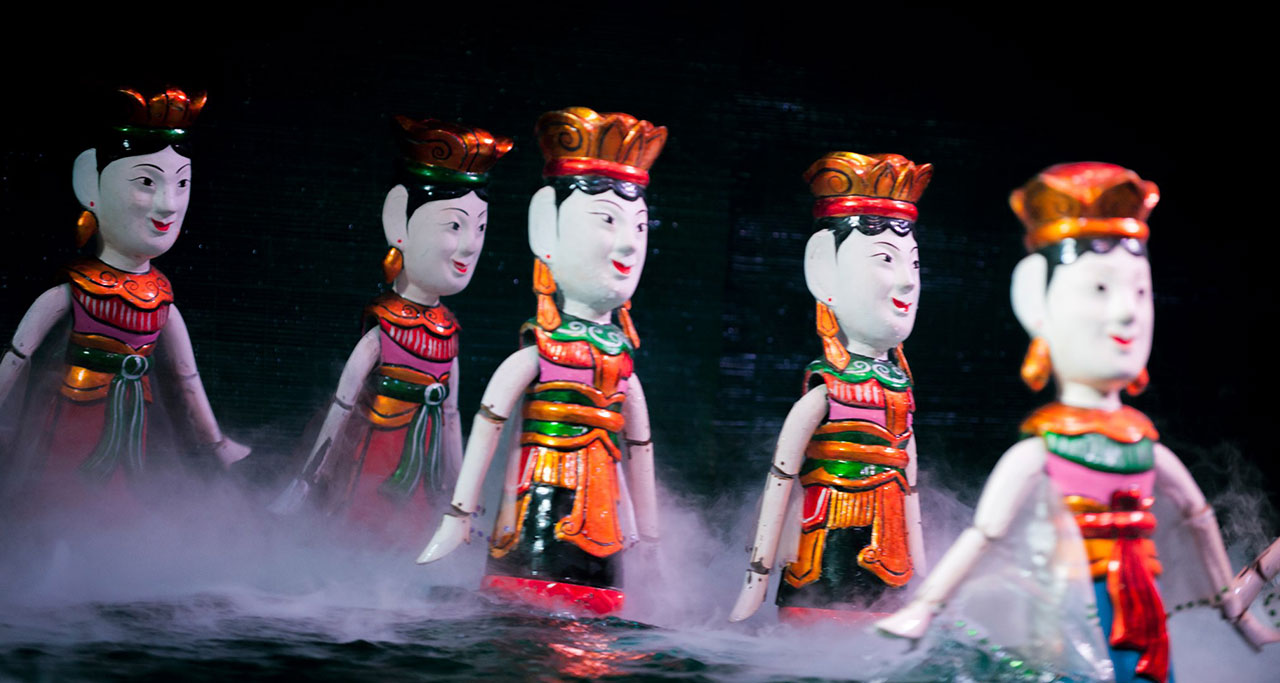

Water puppet show – a traditional art form in Vietnam
Water puppetry is the most popular art genre as well as a typical cultural feature of Vietnam’s wet rice civilization. Its origins dated back to the 12th century, created by Zen Master Tu Dao Hanh. In the performance, a pond or a waist deep pool is used as the stage with puppets made of lacquered wood controlled by puppeteers standing behind the scene.
The show tells the story about traditional scenes of Vietnamese life. Until today, it is still largely enjoyed by many tourists to Vietnam.
Read more: Vietnamese water puppets
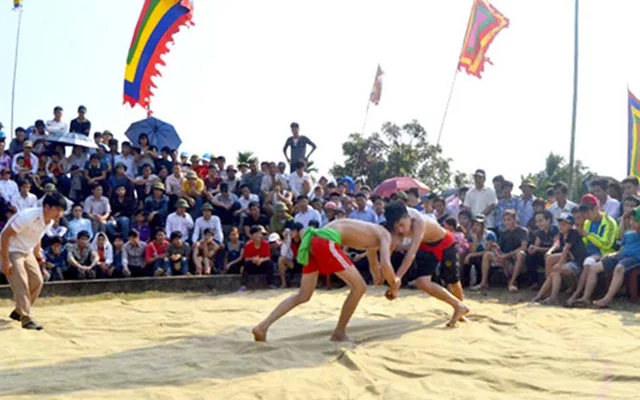
Material Arts
Together with long history of expanding the border and defending the country, traditional martial arts have been an indispensable feature when it comes to Vietnamese culture. These martial arts are the traditional cultural heritage of Vietnam, created by Vietnamese or Vietnameseized from the borrowed martial arts worldwide, to make them suitable with the Vietnamese’s state, culture, and philosophy.
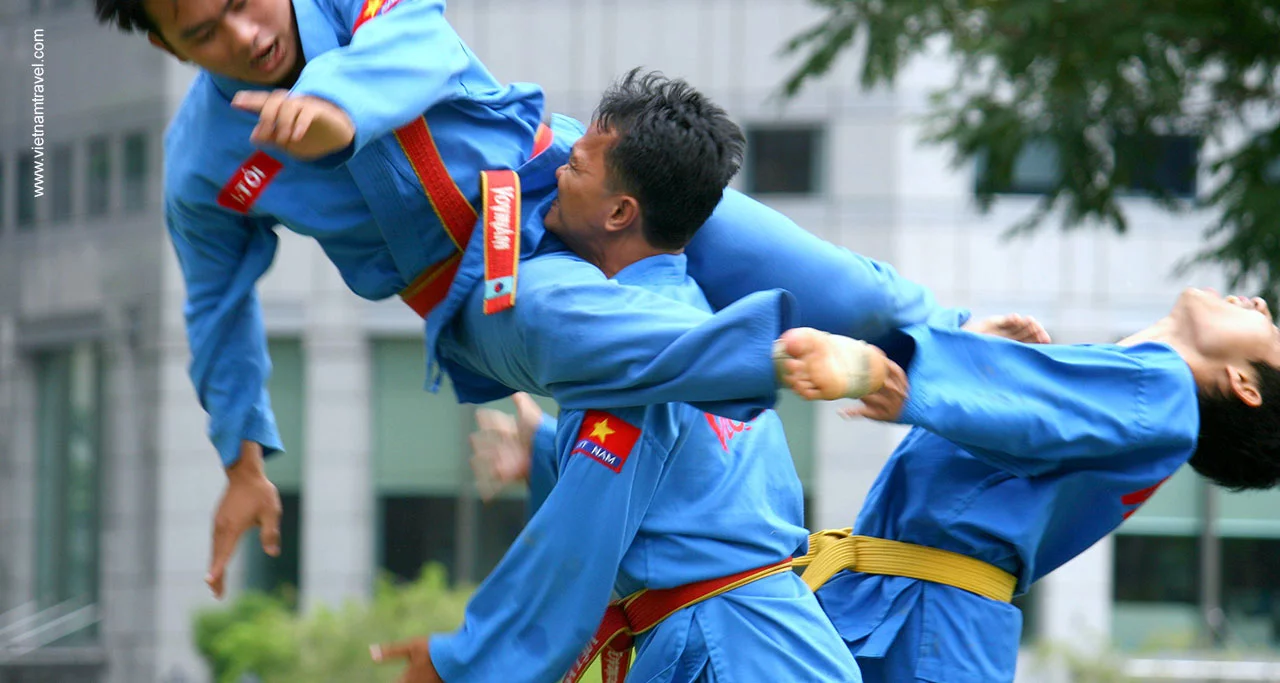

Vovinam – one of most popular traditional Vietnam material arts
There are 5 sects in traditional Vietnam material arts, including Ha Thanh Group (North), Binh Dinh Group (Central), Southern Group (South), Sects originating from China and Vietnamese martial arts overseas.
Some famous sects can be listed here, such as Thien Mon Dao, Thang Long Vo Dao, Nam Hong Son, Nhat Nam, Hoa Quyen, Thanh Phong Vo Dao, Viet Vo Dao, traditional wrestling (North); Tay Son Nhan, Binh Dinh Sa Long Cuong, Binh Dinh martial arts, Tan Son Bach Long, Tay Son Thieu Lam, Binh Dinh Gia, Tien Long Quyen Dao, Tan Khanh Ba Tra in Khanh Hoa, Tan Gia Quyen (Central) or Tan Khanh Ba Tra, That Son Quyen (An Giang), Am Duong Vo Phai, Kim Ke, Thanh Long Vo Dao (South).
Language arts

Vietnamese language arts include literature, poetry. There are 2 types of forms in oral and written. Followed long history under Chinese domination, much of the written works was in Classical Chinese during this period until around 10th century when chu nom was created which allowed writers to compose in Vietnamese using modified Chinese characters.
Before French colonial rule, Vietnamese literature was divided into 2 styles of a classical style based on the Chinese model in the form of poetry, history, essays, and a vernacular one based on local themes and genres which was written in chu nom and took the form of poetry or verse novels. By the middle of 20th century, all Vietnamese works of literature were virtually composed in quoc ngu.
Some defining works of language arts can be listed, such as:
+ Classic Chinese: Nam Quoc Son Ha by General Ly Thuong Kiet, Dai Viet Su Ki by Le Van Huu, Binh Ngo Dai Cao by Nguyen Trai…
+ Chu Nom: The Tale of Kieu by Nguyen Du, Luc Van Tien by Nguyen Dinh Chieu, Chinh Phu Ngam by Doan Thi Diem, Quoc Am Thi Tap by Nguyen Trai, poems by renowned poet Ho Xuan Huong…
+ Modern literature: Viet Nam Su Luoc by Tran Trong Kim, So Do by Vu Trong Phung…
Cinema

The cinema of Vietnam originated in the 1920s and had largely been shaped by wars from the 1940s to the 1970s. In recent years, when Vietnam’s film industry has modernized and moved further, contemporary Vietnamese filmmakers have gained a wider audience. There is a variety of genres from documentary, history to modern films and the contents are also diversified with lots of choice to approach. For young generation, the introduction of movie theatres with good quantity and quality in Vietnam attracts a lot of interests, such as CGV, Lotte, Platinum Cineplex, Galaxy, BHD Star Cineplex. Film festivals taking place in Vietnam also present the continuous development of Vietnam cinema in domestic market and will gradually take greater steps to join in the general cinema of the world.
Obviously, Vietnamese art is represented in many forms, genres and contents. It shows the strong development of Vietnam culture in its long history as well as brings the Vietnamese souls, elites to the world.
Vietnam Travel will be glad if becoming a part of your memorable journey in Vietnam. Our experienced team will show you the best parts of Vietnamese arts for your deeper experience during the trip with us. Let’s contact at any time for our prompt assistance and services!
 Italiano
Italiano
 English
English